About CBD

What is CBD?
CBD = Cannabidiol
a phytocannabinoid (cannabinoid produced in the hemp plant)
a non-addictive, and non-intoxicating hemp compound
a chemical that helps regulate and balance a number of biological functions
it interacts with our body's receptors to produce numerous therapeutic effects
it is one of 113 identified cannabinoids
CBD has no psychoactive properties
Interesting fact: CBD was discovered in 1940
Add a description for this hero banner. This is a great place to highlight a promotion.
How does CBD work?
CBD works with the endocannabinoid system within our body CBD does not directly attach itself to CB1 and CB2, but influences them
activating these receptors is what allows for many of the health benefits that people experience when using CBD
Interesting fact: ECS was discovered in the 1990s
Add a description for this hero banner. This is a great place to highlight a promotion.
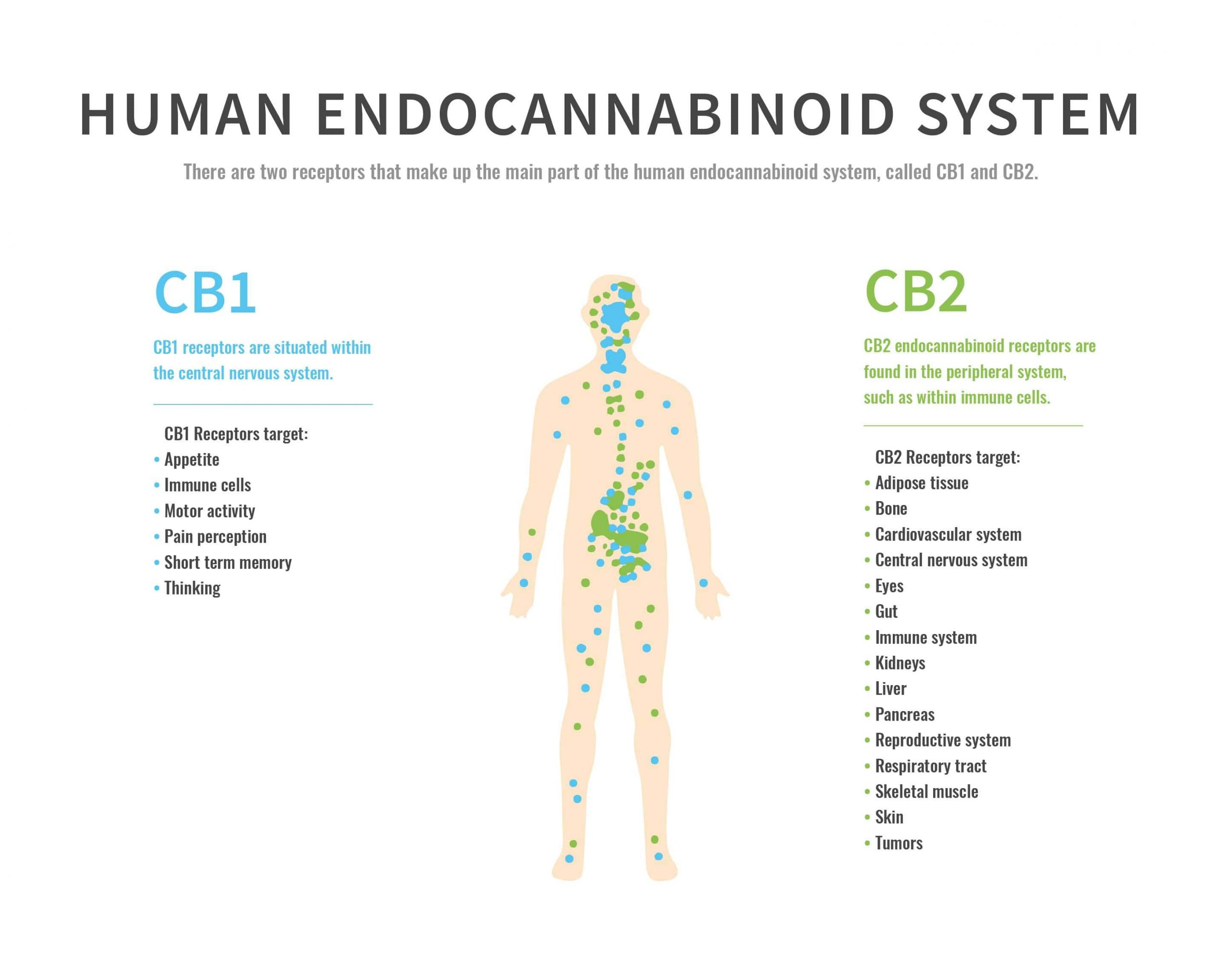
Endocannabinoid System
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS)'s primary role is to maintain homeostasis (maintaining stability of your internal environment)
ECS influences:
-appetite and digestion
-metabolism
-inflammation and other immune system responses
-mood
-learning and memory
-motor control
-sleep
-cardiovascular system function
-muscle formation
-bone remodeling and growth
-liver function
-stress

Reported by the WHO
“In humans, CBD exhibits no effects indicative of any abuse or dependence potential…. To date, there is no evidence of public health related problems associated with the use of pure CBD.”*
*Source: Expert Committee on Drug Dependence, Fortieth Meeting
Geneva, 4-7 June 2018

From the USA Department of Health and Human Services
The United States of America as represented by the Department of Health and Human Services confirm in the US Patent #6630507 that “cannabinoids have been found to have antioxidant properties.”
The patent continues, “This new found property makes cannabinoids useful in the treatment and prophylaxis of wide variety of oxidation associated diseases, such as ischemic, age-related, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.”
Continuing, this patent states, “Nonpsychoactive cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD), are particularly advantageous to use because they avoid toxicity.” The patent continues to confirm “No signs of toxicity or serious side effects have been observed following chronic administration of cannabidiol (CBD) to healthy volunteers, even in large acute doses of 700mg/day.” The United States of America owns this patient and confirms “The present invention is believed to be particularly beneficial in the treatment of oxidative associated diseases of the CNS.”


CBD Research
Pain
The Endocannabinoid System, Cannabinoids, and Pain
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3820295/
Role of the Cannabinoid System in Pain Control and Therapeutic Implications for the Management of Acute and Chronic Pain Episodes
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2430692/
Cannabinoids suppress inflammatory and neuropathic pain by targeting a3 glycine receptors
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3371734/
Inflammation
Cannabinoids as novel anti-inflammatory drugs
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828614/
Cannabidiol as an Emergent Therapeutic Strategy for Lessening the Impact of Inflammation on Oxidative Stress
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3085542/
Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Cannabidiol: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7023045/
Anxiety
Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety Disorders
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4604171/
Cannabidiol in Anxiety and Sleep: A Large Case Series
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6326553/
Sleep
Cannabinoids, Endocannabinoids and Sleep: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7388834/
Cannabidiol in Anxiety and Sleep: A Large Case Series: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6326553/
Autoimmune diseases, MS
Pathways and gene networks mediating the regulatory effects of cannabidiol, a nonpsychoactive cannabinoid, in autoimmune T cells
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4891926/
Cannabidiol to Improve Mobility in People with Multiple Sclerosis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5874292/
Cannabidiol provides long-lasting protection against the deleterious effects of inflammation in a viral model of multiple sclerosis: A role for A2A receptors - ScienceDirect
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969996113001939
Parkinson's Disease
Cannabidiol for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson's disease
Cannabidiol for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson's disease - PubMed (nih.gov)
Is cannabidiol the ideal drug to treat non-motor Parkinson's disease symptoms?
Is cannabidiol the ideal drug to treat non-motor Parkinson’s disease symptoms? | Request PDF (researchgate.net)
Cannabinoids in Late Life Parkinson's Disease and Dementia: Biological Pathways and Clinical Challenges
Cannabinoids in Late Life Parkinson's Disease and Dementia: Biological Pathways and Clinical Challenges - PubMed (nih.gov)
Arthritis
Transdermal cannabidiol reduces inflammation and pain-related behaviours in a rat model of arthritis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4851925/
